The Secret to Weight Loss: The Ultimate Good Macros to Lose Weight Guide
-
 Written by
Michael J. Ormsbee
Written by
Michael J. Ormsbee
- LAST UPDATED September 21, 2023
Weight loss is often approached through a variety of methods. One strategy that’s gaining popularity is counting and optimizing macronutrients for improved health and weight loss. In this guide, learn the basics of macronutrients, how they impact weight loss, and how to choose the best sources for a balanced diet.
Understanding Macros
What are macronutrients?
Macronutrients, frequently shortened to “macros,” represent the substantial groupings of nutrients that our bodies require in considerable quantities. Their primary role is to be the prime source of energy, which is utilised for different aspects such as growth, development, and to power a variety of bodily functions. The trio that forms the foundation of all macronutrients consists of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Functions of Macronutrients and Their Impact on Weight Management
1. Carbohydrates
As the body’s primary source of energy, carbohydrates fuel various bodily processes including brain functioning, physical exertion, and everyday activities. When the aim is weight loss, reducing carbohydrate intake is often a useful strategy, as it can contribute to a decrease in total caloric consumption.
2. Proteins
Proteins are fundamental elements for the construction and repair of tissues, muscles, and body organs. In the context of weight loss, proteins have a prominent role in promoting feelings of fullness, reducing hunger pangs, and maintaining lean muscle mass during the fat loss process.
3. Fats
Fats, besides offering essential fatty acids, play a supportive role in the absorption of vitamins. Healthy fats, including monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can enhance perceptions of fullness, stimulate a well-functioning metabolism, and help uphold a balanced hormonal state. All these factors point to the crucial role that fats play in weight maintenance strategies.
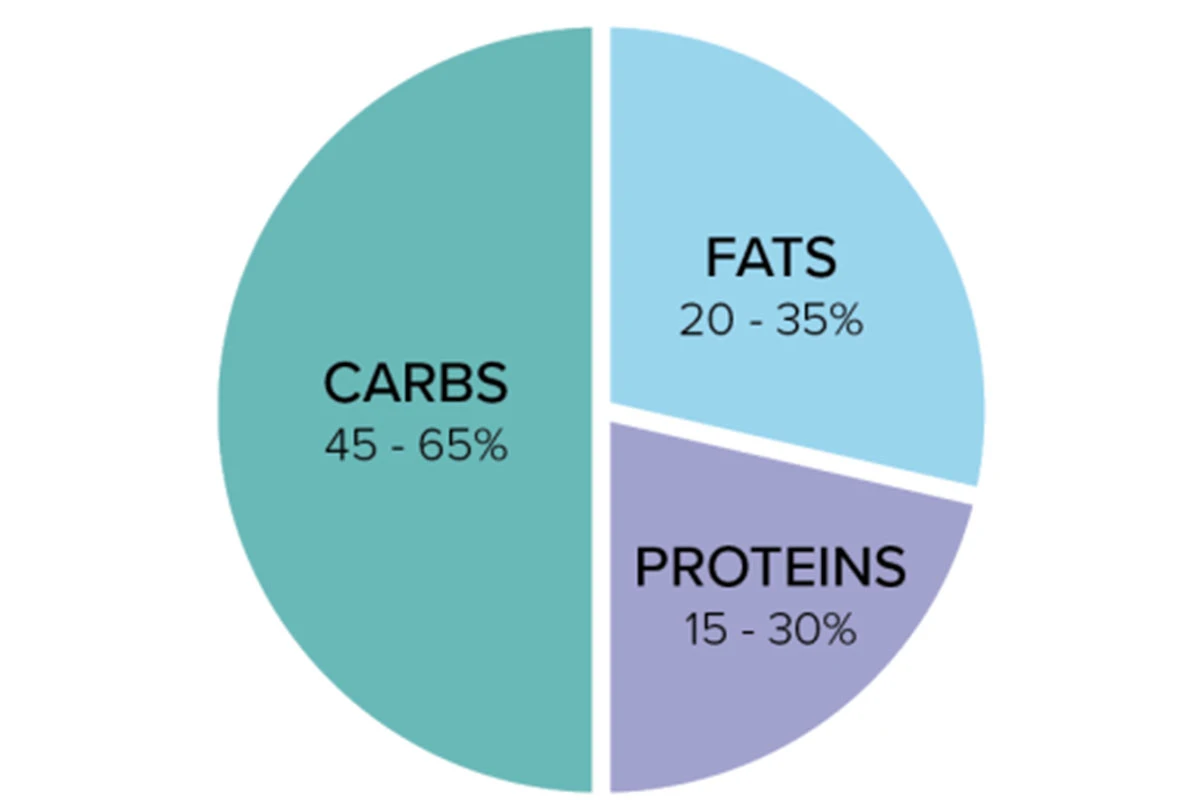
Macro Ratios for Weight Loss: A Comprehensive Overview
The distribution of macronutrients (carbohydrates, proteins, and fats) in a person’s diet can considerably influence their weight loss outcomes. The ideal macro ratio varies from person to person, often based on individual factors and responses to specific dietary approaches.
The Role of Macro Distribution in Weight Loss
Depending on their unique body type, metabolism, and preferences, some individuals tend to achieve better weight loss results by following a low-carb, higher-fat diet. Conversely, others may find balanced ratios across all macronutrients to be more effective. The key is to identify the optimal macro distribution for one’s body and lifestyle in order to maximize weight loss results.
General Guidelines for Macro Ratios in Weight Loss Diets
When it comes to establishing macro ratios that support weight loss, a common starting point is often based on the following percentages:
- 45% Carbohydrates: This percentage provides a moderate carbohydrate intake, giving the body enough fuel for necessary bodily functions while still being low enough to encourage weight loss.
- 25% Protein: A slightly elevated percentage for protein intake helps promote satiety, preserve lean muscle mass, and boost overall weight loss results.
- 30% Fats: Including 30% healthy fats in the diet supports hormonal balance, nutrient absorption, and satiety, contributing to more effective weight management.
It’s essential to remember that these ratios serve as initial guidelines and can be fine-tuned according to specific individual requirements, preferences, and objectives. Factors influencing the need to adjust macro ratios might include one’s level of physical activity, dietary restrictions, age, or pre-existing medical conditions.
Regularly monitoring progress, reflecting on personal experiences, and adjusting the macro ratios accordingly are critical steps towards finding the most effective weight loss strategy tailored to each person’s unique situation.

How to Determine Your Macronutrient Needs: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating your macronutrient needs involves two primary steps – firstly, estimating your daily energy requirements, and secondly, calculating your macro intake based on your daily caloric needs and premeditated macro ratio.
Step 1: Calculating Your Daily Energy Expenditure
Your daily energy expenditure refers to the total number of calories your body needs daily to maintain your current weight. This calculation involves considering various factors including your age, gender, current weight, height, and level of physical activity.
You can use online tools, known as Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) calculators to get this estimate. Alternatively, you can engage the help of a nutritionist or dietitian to personalize these calculations based on your individual characteristics and lifestyle.
Step 2: Determining Your Macro Intake
Once your daily caloric needs have been estimated, the next step is to use your selected macro ratio to calculate your specific intake for each macronutrient.
Let’s illustrate this with an example, where your daily caloric requirement is 2,000 calories and the macro ratio you are adhering to is 45% carbohydrates, 25% protein, and 30% fats:
Carbohydrates:
- First, calculate the total calories from carbs: 45% of 2,000 calories equals 900 calories.
- Then, convert those calories into grams. Since each gram of carbohydrate provides around 4 calories, you would divide 900 calories by 4. The result is 225 grams of carbohydrates.
Proteins:
- Start by finding out the total calories from protein: 25% of 2,000 calories equals 500 calories.
- Next, convert this caloric value into grams, considering that each gram of protein offers around 4 calories. Divide 500 by 4 to get 125 grams of protein.
Fats:
- Initially, calculate the total calories from fats: 30% of 2,000 calories results in 600 calories.
- Finally, convert the caloric value into grams. Since each gram of fat gives about 9 calories, dividing 600 by 9 gives you around 67 grams of fats.
This step-by-step procedure can help you plan your diet effectively according to your personalized macronutrient needs, thus enhancing the success of your weight loss or maintenance goals.
Selecting Nutritious Sources of Macros: A Detailed Review
In order to promote both weight loss and generally good health, it’s important not only to focus on the quantity of your macros, but also the quality. Here’s a detailed guide on choosing the most nutritious sources within each macronutrient category:

Complex Carbohydrates
Rather than opting for simple carbs that are refined and lack essential nutrients, your diet should primarily consist of complex carbohydrates. These nutrient-rich carbs help maintain steady blood sugar levels, keeping you satiated for longer and reducing cravings. They include:
- Whole grains: Foods like brown rice, oats, whole wheat bread, and quinoa not only provide energy but are also packed with fiber, which aids digestion and satiety.
- Fruits and vegetables: These include nutrient-dense items like apples, oranges, leafy greens, and bell peppers, all of which are packed with essential vitamins and minerals.
- Legumes: Foods such as chickpeas, lentils, and black beans are a great source of both carbohydrates and protein, making them a powerful asset for weight management.
Lean Proteins
Opt for lean protein sources which have fewer calories and less fat compared to their full-fat counterparts:
- Poultry: Chicken and turkey are excellent sources of lean protein.
- Seafood: Fish, especially fatty fish like salmon and mackerel, are loaded with protein and provide valuable omega-3 fatty acids.
- Lean red meat: Choose cuts of beef and pork that are low in fat, such as sirloin or tenderloin.
- Plant-based proteins: Options like beans, lentils, tofu and tempeh are fantastic sources of protein and suitable for vegetarian or vegan diets.
Healthy Fats
Not all fats are bad. In fact, some types of fat are incredibly beneficial for your health:
- Avocado: Unlike most fruits, avocados are high in healthy fats instead of carbs. They also contain a fair amount of fiber and essential nutrients.
- Olive oil: A primary component of the Mediterranean diet, olive oil is praised for its heart-healthy properties.
- Nuts and Seeds: Walnuts, almonds, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are rich in healthy fats and also fiber and protein.

Effective Management of Macro Intake: Tracking and Adjustments
Regularly monitoring and adjusting your macronutrient intake is crucial to achieve your weight loss goals. Here’s a more detailed look into this process.
Monitoring Your Macronutrient Intake
Accurately tracking your food consumption is the first step toward balancing your macronutrient consumption. Here’s how you can approach it:
- Food Applications: There are numerous food applications available that can help track your daily macro intake. Applications such as MyFitnessPal or Cronometer let you log in completed meals along with their portion sizes. These apps automatically calculate the calorie and macro content of each item, making it easier to ensure you are hitting your specific target goals.
- Food Diary: In case you do not wish to use food apps, maintaining a manual food diary can also serve this purpose. Document each meal, along with estimated portion sizes, and calculate the macronutrient content accordingly. For this, you may need to refer to the nutritional information provided on food packaging or use online nutrition databases.
- Digital Food Scale: To increase the accuracy of your tracking, consider using a digital food scale. This tool can give a precise measure of your food portions, enabling you to calculate more accurate macro numbers.
Adjusting Your Macronutrient Intake
Over time, you might find it necessary to adjust your macro ratios to better match your changing needs and responses. Here are some considerations:
- Changes in Activity Levels: An increase or decrease in physical activity can significantly impact your dietary needs. More activity generally implies the need for more fuel, commonly needing higher proportions of carbohydrates and protein. Likewise, if your activity levels decrease, you may need to lower your overall calorie intake to avoid gaining weight, mainly adjusting from carbohydrate and fat sources.
- Hitting a Weight Loss Plateau: If you find that your progress has stunted despite adhering to your planned macro ratios, this could indicate a need for adjustment. Consider decreasing your carbohydrate ratio and increasing protein for a period to jumpstart your metabolism and induce further weight loss.
- General Health and Well-being: Always pay attention to how you feel. If you’re constantly tired, hungry, or falling sick, it might be a sign that you’re not meeting your body’s nutritional needs properly. In such cases, consider consulting with a nutrition professional to reassess your diet plan.
Tips for Macro Dieting Success
Adhering to a macro-based diet can significantly enhance your ability to manage body weight and obtain health benefits. Let’s delve deeper into practical strategies to maximize your success.
Setting Realistic Goals and Emphasizing Long-term Changes
As you embark on your macro dieting journey, it’s pivotal to set attainable goals that will motivate you without causing frustration.
- Primarily aim for sustainability: Rapid weight loss can be enticing; however, it often involves restrictive diets that can be hard to maintain in the long run and may lead to rebound weight gain. Therefore, focus on forming long-term, sustainable eating habits that will enable gradual but sustained weight loss.
- Set measurable own goals: Instead of vague ambitions like ‘losing weight’, be more specific. This could involve setting a particular weight loss aim for a specified period or trying to incorporate certain positive health behaviours, such as ‘Incorporate 5 servings of vegetables daily’.
Consistent Tracking and Adjusting of Macros
To optimize your weight loss results, being consistent and adaptable in managing your macro intake is crucial.
- Incorporate regular monitoring practices: Whether it’s a digital application or traditional food diary, ensure you log your food intake consistently. It’s this regular monitoring that will give you a realistic picture of your current eating pattern and guide your macro adjustments.
- Be flexible in adjustments: Our bodies are not static and neither should be our diet. Adjusting your macro ratios in response to changes in goal, lifestyle, or bodily responses can help keep you on track and prevent weight loss plateaus.
Collaborating with Health Professionals
Don’t shy away from seeking professional guidance during your macro dieting voyage.
- Consult a dietitian: A registered dietitian can provide personalized macro targets and meal plans according to your specific needs and lifestyle. They can also help you through any crucial nutrition-related queries or hurdles you encounter in the process.
- Engage a personal trainer: If you’re incorporating exercise into your weight management strategy, a personal trainer can provide tailored exercises, support you in maintaining an optimal activity level, and guide about necessary dietary changes based on your exercise regimen.

Frequently Asked Questions on Good Macros for Lose Weight
1. What should my daily macros be to lose weight?
To lose weight, focus on creating a calorie deficit while maintaining an optimal macro ratio. The appropriate ratio varies depending on individual factors such as age, gender, activity level, and body composition. However, a general guideline is:
- Protein: 25-30% of total calories
- Carbohydrates: 40-50% of total calories
- Fats: 25-35% of total calories
2. How do I calculate my macros to lose fat?
To calculate your macros for losing fat:
- Determine your daily calorie needs using a TDEE (Total Daily Energy Expenditure) calculator.
- Subtract a conservative number of calories (around 300-500) to create a calorie deficit.
- Divide the remaining calories among your macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fats) using your preferred macro ratio.
3. Is a 50-30-20 macro ratio good?
A 50-30-20 macro ratio implies allocating 50% of your calories to carbohydrates, 30% to protein, and 20% to fats. This may be an effective ratio for some people, particularly those engaging in moderate to high-intensity exercise. Always consult a healthcare professional to determine if this ratio is suitable for your personal needs.
4. Is a 50-25-25 macro ratio good?
A 50-25-25 macro ratio (50% carbohydrates, 25% protein, and 25% fats) may be suitable for some people. However, the optimal macro ratio depends on personal factors, including individual goals and lifestyles. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
5. What does a 40-30-30 macro ratio look like?
A 40-30-30 macro ratio entails allocating 40% of your daily calories to carbohydrates, 30% to protein, and 30% to fats. For example, if you consume 2000 calories daily, you would aim for:
- Carbohydrates: 200g (800 calories)
- Protein: 150g (600 calories)
- Fats: 67g (600 calories)
6. What is the best macro ratio for fat loss?
There is no universal "best" macro ratio for fat loss, as the ideal mix fluctuates depending on personal factors. Aim for a calorie deficit while maintaining a balance of macronutrients. Many people find success with a higher protein ratio (25-30%) and a moderate distribution of carbohydrates and fats (40-50% carbs, 25-35% fats). Consult a healthcare professional for personalized recommendations.